Levels of College Knowledge: Introductory & Advanced

Not all of the learning you gain in college is at the same level. Colleges often sequence courses so that you can build depth of knowledge in a field.
For example, you might take an introductory management course before taking a course in Organizational Behavior, since the Organizational Behavior course builds on introductory management knowledge. In the same way, you might take Introduction to Psychology before taking Social Psychology or Theories of Personality.
When you’re taking college courses, it’s relatively easy to tell which courses are introductory and advanced by the course numbering system and whether the course description lists prerequisites.
On the other hand, it’s more difficult to determine the knowledge level of experiential learning, since you often don’t gain that type of learning in a prescribed sequence. So you need other ways to consider the depth or level of your experiential learning.
Use Bloom’s Taxonomy to investigate Level of Learning
Introductory and advanced level credit can be related to Bloom’s revised taxonomy.
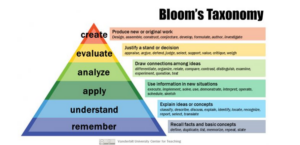
Introductory Level
- Remember: Recall facts and basic concepts
- Understand: Explain ideas or concepts
- Apply: Use information in new situations
Advanced Level
- Analyze: Draw connections among ideas
- Evaluate: Justify a stand or decision
- Create: Produce new or original work
Use The Global Learning Qualifications Framework to investigate Level of Learning

The Global Learning Qualifications Framework (GLQF) is a resource that identifies three main aspects of college-level knowledge – Integration, Knowledge, and Engagement.
Within these three broad areas, there are eight more specific areas that list additional characteristics. Each word for each characteristic is a link that will take you to more information that describes this characteristic of college-level knowledge.
You will find definitions, questions that describe each characteristic, examples that yield this type of learning, and characteristics of introductory- and advanced-level learning (freshman/sophomore vs. junior/senior).
